Major Food Distributor in Peril: Play Ransomware Threatens to Unleash Chaos at Associated Wholesale Grocers
The Play ransomware group has threatened the Associated Wholesale Grocers (AWG), a major player in the food distribution industry. The threat actors have declared their intention to release AWG’s sensitive data on October 22, 2023. This Associated Wholesale Grocers cyberattack notification came to light through a message posted on their clandestine dark web channel.
The data allegedly contains a trove of sensitive information including private and confidential data, client documents, contracts, social security numbers, passports, payroll details, tax records, financial information, and more. The publication date is ominously set just three days from now, heightening the urgency of the situation.
Play Ransomware Asserts Associated Wholesale Grocers Cyberattack
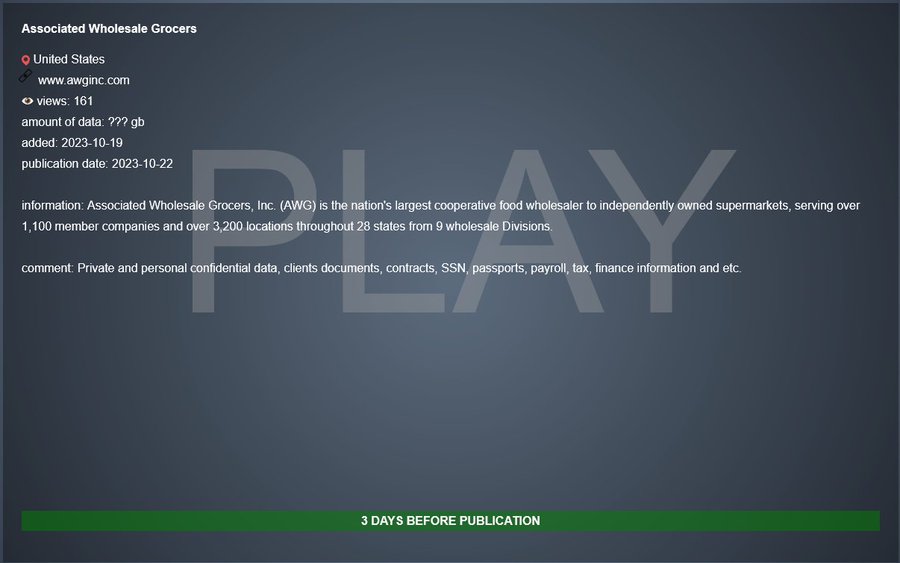
Associated Wholesale Grocers, Inc. (AWG), renowned as the largest cooperative food wholesaler to independently owned supermarkets in the United States, is currently serving over 1,100 member companies and spanning more than 3,200 locations in 28 states through its nine wholesale divisions.
The Cyber Express made attempts to contact AWG to glean more insights into this purported Associated Wholesale Grocers cyberattack. However, communication hurdles obstructed our path, leaving us with more questions than answers.
Aside from this Associated Wholesale Grocers cyberattack, the Play ransomware group has been on a rampage, targeting managed service providers (MSPs) worldwide. This campaign aims to disseminate ransomware to downstream customers, amplifying the potential fallout.
Who is the Play ransomware group?
Play” is the moniker of a particularly wicked strain of ransomware. This breed of malware specializes in encrypting data, holding it hostage until a ransom is paid for its release. The implications of such an attack can be devastating, as it can paralyze critical operations and jeopardize sensitive information.
One particularly insidious facet of this campaign is the use of intermittent encryption. Rather than encrypting entire files, the threat actors target specific sections, a tactic designed to slip past detection algorithms.
Play ransomware’s crosshairs are fixed on mid-sized enterprises in various sectors, including finance, legal, software, shipping, law enforcement, and logistics. Their operations have been spotted in countries like the United States, Australia, the United Kingdom, and Italy. Additionally, state, local, and tribal entities in these nations have not been spared.
Modus Operandi of Play Ransomware Group
Infiltrating MSP systems is a key strategy for Play. Once inside, they exploit remote monitoring and management (RMM) tools to gain unfettered access to the networks and systems of the MSPs’ customers.
This modus operandi has proven alarmingly effective, as evidenced by previous incidents involving different threat actors.
Towards the close of 2022, Play demonstrated a new technique, exploiting two ProxyNotShell vulnerabilities in Microsoft Exchange for initial access.
These vulnerabilities, despite being patched by Microsoft in November 2022, remained exploitable due to Play’s ability to bypass URL rewrite mitigations.
Media Disclaimer: This report is based on internal and external research obtained through various means. The information provided is for reference purposes only, and users bear full responsibility for their reliance on it. The Cyber Express assumes no liability for the accuracy or consequences of using this information.